A research team from Osaka City University in Japan have succeeded in treating skin ulcers caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria using 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and LED lights, according to a Nikkei Technology report.
The group’s treatment trials on mouse with methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infected skin ulcers were effective, and did not cause the emergence of resistant bacteria.
 |
|
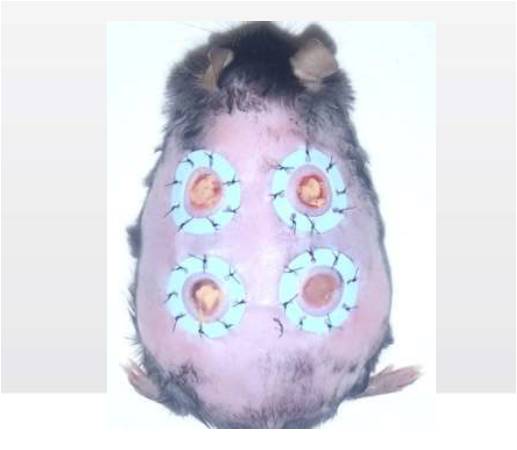
The mouse used in the sutdy has skin ulcers infected with MRSA on its back. (Photo Courtesy of Nikkei Technology) |
MRSA is a type of bacteria that is resistant to most antibiotics, and has become a major global issue in the medical field where skin infections caused by the bacteria are particularly difficult to cure and can even cause death.
The group administered the treatment to a mouse infected with skin ulcers infected with MRSA on its back. The ALA a substance that give photosensitivity was applied with PDT using a blue-violet LED light source at a wavelength of 410 nm. The PDT is a treatment that destroys targeted cells with reactive oxygen generated by applying a light with a specific wavelength after concentrating photo-sensitive substances on the target issue.
The research team’s results were published on the US online journal PLOS ONE under the title "Photodynamic therapy using systemic administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid and 410-nm wavelength light emitting diode for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infected ulcers in mice."












