Researchers from KAIST published their research on developing a one-step method to transfer thousands of thin-film blue vertical micro LEDs (thickness < 2 μm) on a transparent plastic substrate.

(Image: KAIST)
Earlier this year, the Korean research team revealed its development of flexible red vertical Micro LED (f-VLEDs). Comparing to flexible lateral Micro LED, f-VLEDs achieved three times higher optical power density (30 mW/mm2) and a lifetime of 100,000 hours (approximately 12 years) by reducing heat generation. With the most updated investigation, researchers demonstrated ultrathin vertical GaN LED arrays with one-time transfer method; the technology may lead to low cost production of Micro LED.
The blue GaN f-VLEDs could be attached to curved surfaces like skin or even brain stably without mechanical deformation and be driven by wirelessly transferred electrical power. Researchers has practice the experiment to insert the high-density GaN f-VLED onto a living mouse cortex and the operation did not cause significant brain damage.
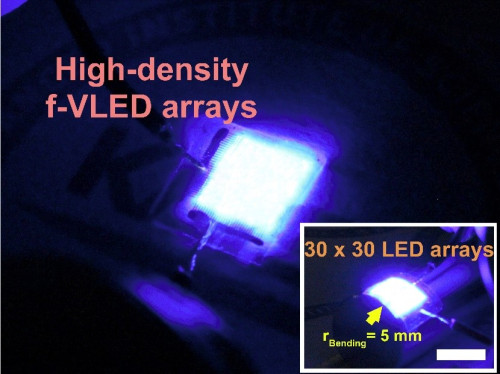
(Image: KAIST)
The KAIST team expects to utilize the technology on wearable devices and plans to demonstrate a full-color Micro LED display in smart watch sizes by the end of 2018.
The research led by Han Eol Lee, “Monolithic Flexible Vertical GaN Light‐Emitting Diodes for a Transparent Wireless Brain Optical Stimulator” was published in the June 2018 issue of Advanced Materials.













