Noise is an issue in optical telecommunications. And findings means of controlling noise is key to physicists investigating light-emitting diodes or lasers. Now, an Italo-Iraqi team has worked on a particular type of light source, called the quantum dot light-emitting diode (QDLED). In a study published in EPJ D, Kais Al Namee from the National Institute of Optics, in Florence, Italy and colleagues, demonstrate that modulating bias current of the QDLED could lead to countering the noise. This, in turn, leads to stabilising such light sources, making them better suited for optical telecommunications.
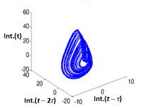 |
Researchers identified noise pattern in QDLED. The next step is to control the noise using bias current. (EPJ D/LEDinside)
|
Most light sources exhibit fluctuations due to the quantum nature of the process underlying the emission of light. However, experiments show that these fluctuations - often described as quantum noise - are inherently chaotic and subject to oscillations, dubbed mixed mode oscillations. The authors have developed a theoretical model, which they show is able to reproduce the chaotic and oscillating phenomena observed experimentally. This can help them understand the nature of such phenomena.
They found that spiking competition of quantum dots in the part of the diode that emits lights enhances the way in which the diode receives its own self-feedback in terms of the light being emitted and it also has an effect on the impact of noise perturbation. They also show that the dynamics of these fluctuations are completely determined by the variation of the injecting bias current feeding into the QDLED.
As a result, Al Naimee and colleagues realised that fluctuations can be brought under control by changing the bias current. The next step in their research will involve focusing on synchronisation phenomena in QDLED arrays for using this source in optical telecommunications. Other potential applications could include quantum dot-enhanced LED-backlighting of LCD televisions.
Original study:
K. Al Naimee, H. Al Husseini, S.F. Abdalah, A. Al Khursan, A. H. Khedir, R. Meucci, F.T. Arecchi (2015), Complex dynamics in Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diodes, Eur. Phys. J. D 69, 257, DOI 10.1140/epjd/e2015-60201-x












