Physicists from the University of Exeter in collaboration with the ICFO Institute in Barcelona have used a ground-breaking new technique to trap light at the surface of the wonder material graphene using only pulses of laser light.
 |
The experimental coupling and arrangement of graphene. (Photo Courtesy of ICFO)
|
Crucially, the team of scientists have also been able to steer this trapped light across the surface of the graphene, without the need for any nanoscale devices. This dual breakthrough opens up a host of opportunities for advances in pivotal electronic products, such as sensors and miniaturised integrated circuits.
The new research features in the latest online edition of the respected scientific journal, Nature Physics.
Dr Tom Constant, lead author on the paper and part of Exeter’s Physics and Astronomy Department said: “ This new research has the potential to give us invaluable insight into the wonder material and how it interacts with light. A more immediate commercial application could be a simple device that could easily scan a piece of graphene and tell you some key properties like conductivity, resistance and purity.”
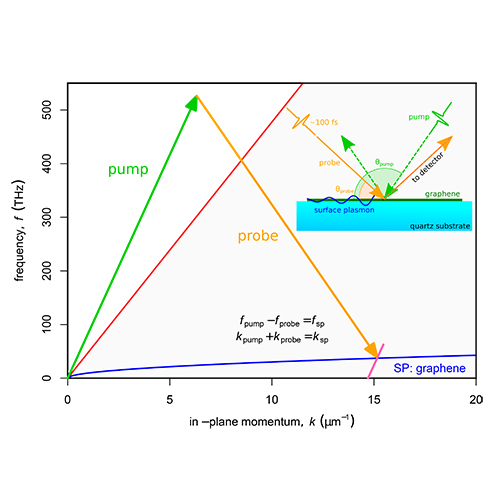
Dr Constant and his colleagues used pulses of light to be able to trap the light on the surface of commercially-available graphene. When trapped, the light converts into a quasi-particle called a ‘surface plasmon’, a mixture of both light and the graphene’s electrons.
Additionally, the team have demonstrated the first example of being able to steer the plasmons around the surface of the graphene, without the need to manufacture complicated nanoscale systems. The ability both to trap light at a surface, and direct it easily, opens up new opportunities for a number of electronic-based devices, as well as help to bridge the gap between the electronics and light.
Dr Constant said: “Computers than can use light as part of their infrastructure have the potential to show significant improvement. Any advance that reveals more about light’s interaction with graphene-based electronics will surely benefit the computers or smartphones of the future.”
The research paper, entitled 'All-optical generation of surface plasmons in graphene' will appear on Nature Physics online on Monday, November 16.





 CN
TW
EN
CN
TW
EN






