A new study published by researchers at Tohoku University in Japan introduced a novel solution for realizing high speed light transmission via deep UV (DUV) LEDs. The results were published in Applied Physics Letters on July 22, 2020.
The research team highlighted two major issues of using LEDs as light source for wireless communication. One thing is that faster modulation requires smaller device size but smaller LEDs usually lack power. Another issue is that both visible and infrared optical wireless communications can have significant solar interference. To avoid confusion with visible and infrared solar light, the researchers aimed to improve LEDs that specifically communicate via DUV light, which can be detected without solar interference.
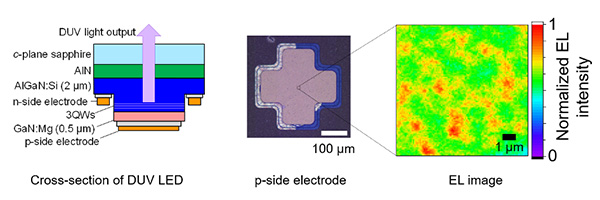
(Kazunobu Kojima, Tohoku University)
The researchers compared the transmission speed between DUV LEDs and conventional LEDs and found that DUV LEDs were smaller and much quicker. Following the results, the team wants to use the DUV LEDs in 5G wireless networks. Many technologies are currently under testing to contribute 5G, and Li-Fi, or light fidelity, is one of the candidate technologies.
"The mechanism underlying this speed is in how a lot of tiny LEDs self-organize in a single DUV LED," said Kazunobu Kojima, associate professor at the Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials at Tohoku University.
Meanwhile, due to the COVID-19 crisis, DUV LEDs have been mass produced for disinfecting applications to prevent the spread of the disease. Kojima also noted that DUV light can serve for sterilization process as well as in solar-blind optical wireless communications.












