2018-11-08
Quantum dot developer Quantum Materials has announced its achievement of testing a 100% cadmium-free remote phosphor quantum dot LED technology that achieved a 91% Rec2020 color gamut coverage. Quantum Materials has been working with several LED producers, display manufacturers and chemical companies with the technology, aiming to bring the new solution to the current industry.
A way for the solution to achieve wide color gamut display is to deposit red and green quantum dots directly on the surface of a blue phosphor driven backlight LED, Quantum Materials has developed...
Continue reading →
 2017-08-18
2017-08-18
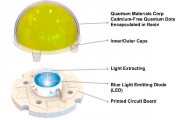
Quantum Materials Corp announced that its cadmium-free quantum dots in a remote LED application successfully surpassed the 1000 hour continuous on-time durability test. The testing has been conducted with red and green quantum dots encapsulated in resin and mounted to blue emitting LED's (see diagram below), which are similar to the type of LED's used in standard LCD display back light units (BLU).
Continue reading →
2016-08-22
Thin fine pitch indoor LED displays have caught on the market in recent years, but a big challenge for the industry is miniaturizing LED suitable for display smaller than 100-inch, said Min-Hsun Hsieh, Vice President (VP) of R&D Center at EPISTAR during a recent interview with LEDinside.
Continue reading →
2016-03-29
Nanoco Group plc , a world leader in the development and manufacture of cadmium-free quantum dots and other nanomaterials, today announced the company will be showcasing its innovative CFQD® Quantum Dot LED lighting at the Indoor Ag-Con conference, taking place April 5-6, 2016 at the Las Vegas Convention Center, Las Vegas, NV (booth #120).
Continue reading →
 2015-08-10
2015-08-10
Recently, quantum dots (QDs)—nano-sized semiconductor particles that produce bright, sharp, color light—have moved from the research lab into commercial products like high-end TVs, e-readers, laptops, and even some LED lighting. However, QDs are expensive to make so there’s a push to improve their performance and efficiency, while lowering their fabrication costs.A team of researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign has recently produced some promising results toward that goal, developing a new method to extract more efficient and polarized light from quantum dots (QDs) over a large-scale area. Their method, which combines QD and photonic crystal technology, could lead to brighter and more efficient mobile phone, tablet, and computer displays, as well as enhanced LED lighting.
Continue reading →
 2017-08-18
2017-08-18
 2015-08-10
2015-08-10