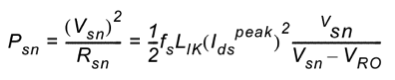PAR16, 20, 30, 38 Lamp LED Driver Design
This is the fifth and final installment of Fairchild Semiconductor's series on LED lighting trends. In this entry, Fairchild Semiconductor experts will address PAR16,20,30,38 lamps. These lamp types are AC voltage input, power rating between 4W~20W, socket is screw type E26/27 or 2 pin type GU10, as shown in Fig. 1.
 |
|
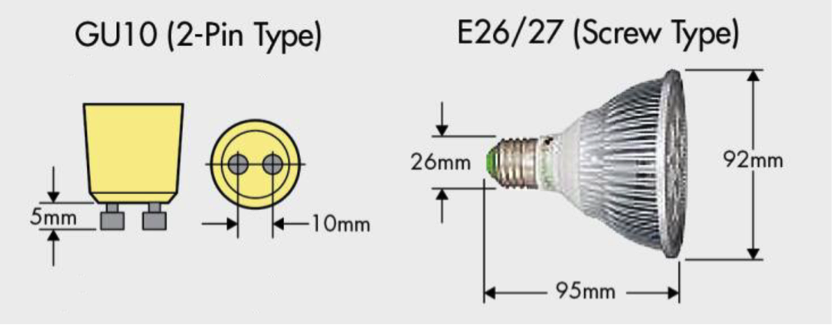
Fig. 1. Example PAR Lamp Dimensions (L: 95mm, D: 92mm, B: 26mm) (All images courtesy of Fairchild Semiconductor) |
With the larger lamp size, there is more space to contain the LED driver solution and PF and low THD are mandatory.
PAR16,20,30,38 Lamp LED Driver Challenges
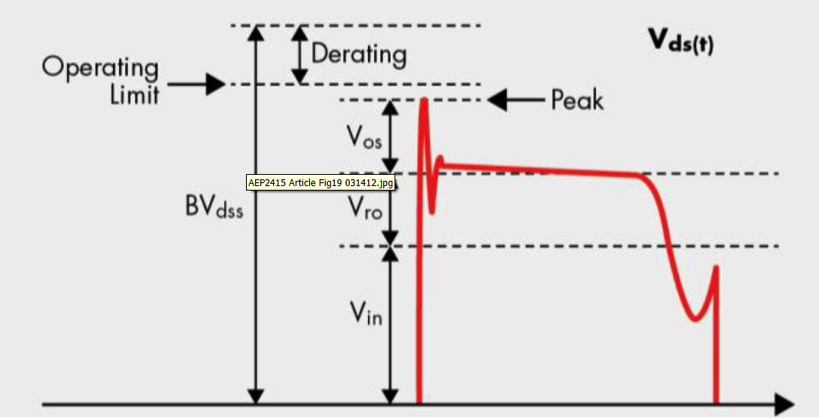
The LED driver designer can chose among the PSR PFC Flyback, a single-stage PFC flyback. However, for this kind Flyback driver, the higher wattage values of these LED lamps can create a higher Vds,peak across the MOSFET, resulting in the need for a higher BVDss-rated MOSFET. The BVDss rating must de-rate for the high-voltage spike. Fig. 2 shows the voltage spike as the sum of Vds,peak = Vin+nVo+Vos where nVo is the reflected output voltage, also known as Vro.
 |
|
Fig. 2. Vds,peak vs. MOSFET Derating |
A snubber is used to limit the Vos peak voltage spike, but the snubber dissipates energy, which decreases the LED driver efficiency:
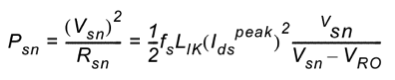 |
|
Formula for LED driver efficacy. |
PAR16,20,30,38 Lamp – Fairchild Solutions
The PSR PFC solution described in the previous blogs is a good choice for this LED driver topology. In certain designs, however, another good solution is the single-stage flyback control PWM IC with CRM PFC. The advantage is less design complexity with good efficiency. Compared with a complex two-stage approach, it provides high PF and low THD and does not require an input electrolytic bulk capacitor. Fig. 3 shows a basic single-stage PFC schematic.
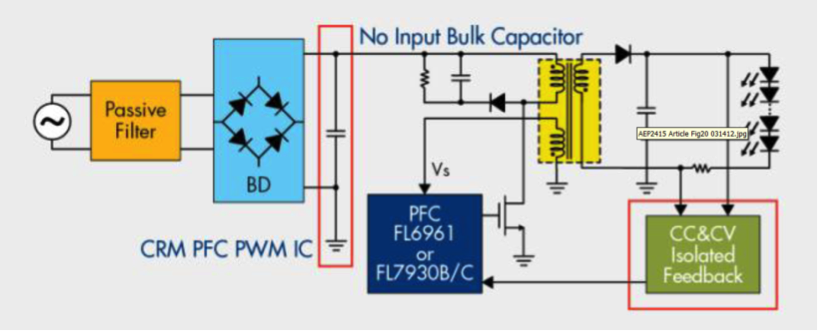 |
|
Fig. 3 Representative Single-Stage PFC Schematic |
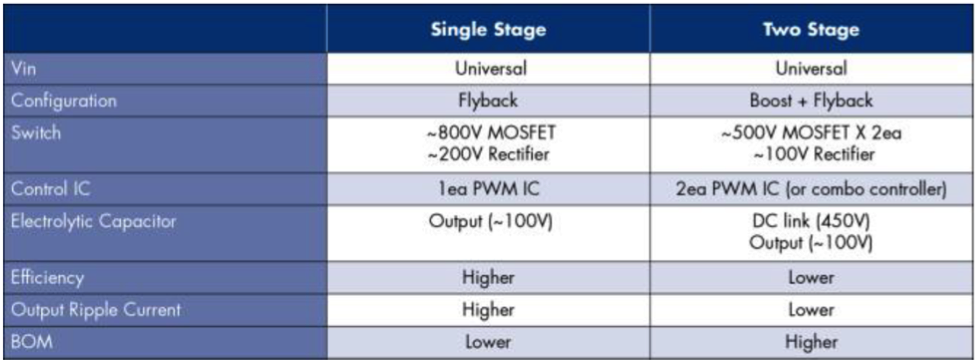
Fairchild solutions are shown in Table 1 with a comparison of single-stage flyback versus a two-stage approach compared in Table 2.
 |
|
Table 1 |
 |
|
Table 2 |
Conclusion
Low-power LED driver applications were reviewed, presenting trends and challenges. Although there are differences in the various types of LED lamps, there are only a few different requirements for the LED driver by lamp type. In general, the basic requirements are similar: a low BOM count and cost, small outline for the PCB, high efficiency, high PF, and low THD. Fairchild solutions include the AC-DC non-isolated PFC buck topology or single-stage PFC primary-side regulation offline topology, reducing the need for multiple suppliers and technology inputs.
Please visit our LED resource page to learn about Fairchild’s LED lighting solutions.
(Authors: James Lee, Brian Johnson and Richard Chung of Fairchild Semiconductor.)
Related Entries: