Mini LED and Micro LED, the novel display technologies based on LED, have lit up the industry which long suffered from low price competition. As worldwide companies and research institutes pouring resources into technology development in the past years and building up partnerships to formulate new ecosystem, several Micro and Mini LED achievements were revealed. Display products using Mini LED backlight are launched and Micro LED prototypes also continue to achieve breakthroughs.

(Image: Pixabay)
Apple’s rumor of launching Mini LED backlight technology adopted iPad and MacBook and working with Taiwan-based Epistar and AUO for Micro LED development with increased investment also brought new hope for the LED industry. Many expect other brands will follow the trend and choose Mini LED, boosting demands for the technology.
As Mini LED and Micro LED continue to evolve, the border line between the two technologies sometimes blurs. LEDinside of TrendForce thus updates the definition for Micro LED and Mini LED following the current technology development and identifies the differences between them. Current challenges and technology analysis of the two innovative display technologies are also presented.
Origin and Definition of Micro LED and Mini LED
Micro LED display technology miniaturizes conventional LED structure to micron/μm scale and removes sapphire substrate. These tiny LEDs in matrix can be controlled pixel by pixel to realize high brightness, resolution, saturation with lower power consumption, delivering advanced display performance.
The prototype of Micro LED technology is Sony’s Crystal LED display presented in 2012. 6.22 million Micro LEDs were used to build the 55-inch display to show an ultra-high resolution. However, the display was created by embedding one single LED after another, which is extremely time consuming and expensive, addressing the manufacture challenges of Micro LED displays.
As the technological barriers of Micro LED display production were too high, Taiwan’s LED chip maker Epistar proposed the idea of Mini LED, which also reduce the size of LED but keep the sapphire substrate. In this way, the LED chips can still be manufactured with current equipment. The cost and difficulties of producing Mini LED are thus lower down, making the technology easier to enter the commercial market.
Back in 2018, LEDinside defined that Mini LEDs are above the size of 100 μm while Micro LEDs are under. But as the technology continues to improve, some companies are able to make Mini LED chips with sapphire substrate that are below 100 μm. As a result, LEDinside redefine that Micro LEDs have to be below 75 μm and without sapphire substrate. And Mini LEDs are between 75 to 300 μm with sapphire substrate.
Features and Current Challenges of Micro LED and Mini LED Display Technology
Despite that some consider Mini LED a transitional phase of display technology on the way moving toward Micro LED, Mini LED has actually positioned in the market as the technology becomes more mature for applications of display backlight sources and RGB fine-pitch displays.
As for backlight applications, Mini LED backlight display enables full array local dimming, realizing a low definition grey-scale-like backlight panel to intensify contrast and resolution of display. Furthermore, the keep shrinking Mini LED chips allow increased dimming zone to enhance display performance.
Another Mini LED application is RGB fine-pitch displays which deploy small size Mini LED packages to create display video walls with pitch size less than 1.0 mm, setting up a new mainstream specification for signage.
Comparing to conventional display applications, Mini LED backlight displays and Mini LED RGB displays use tens of thousands times more LED dies, placing advanced requirement for chip dies sorting and testing, as well as transferring. Although these processes can also be achieved with existing pick and place technology, the speed and yield can hardly compete with new equipment. As a result, LED chip maker Epistar, who largely increased Mini LED capacity this year, focused majorly on back-end manufacture process. The company purchased large amount of transferring and bonding equipment, along with sorting and testing system, aiming to accelerate Mini LED mass production.
Differences between Mini LED and Micro LED
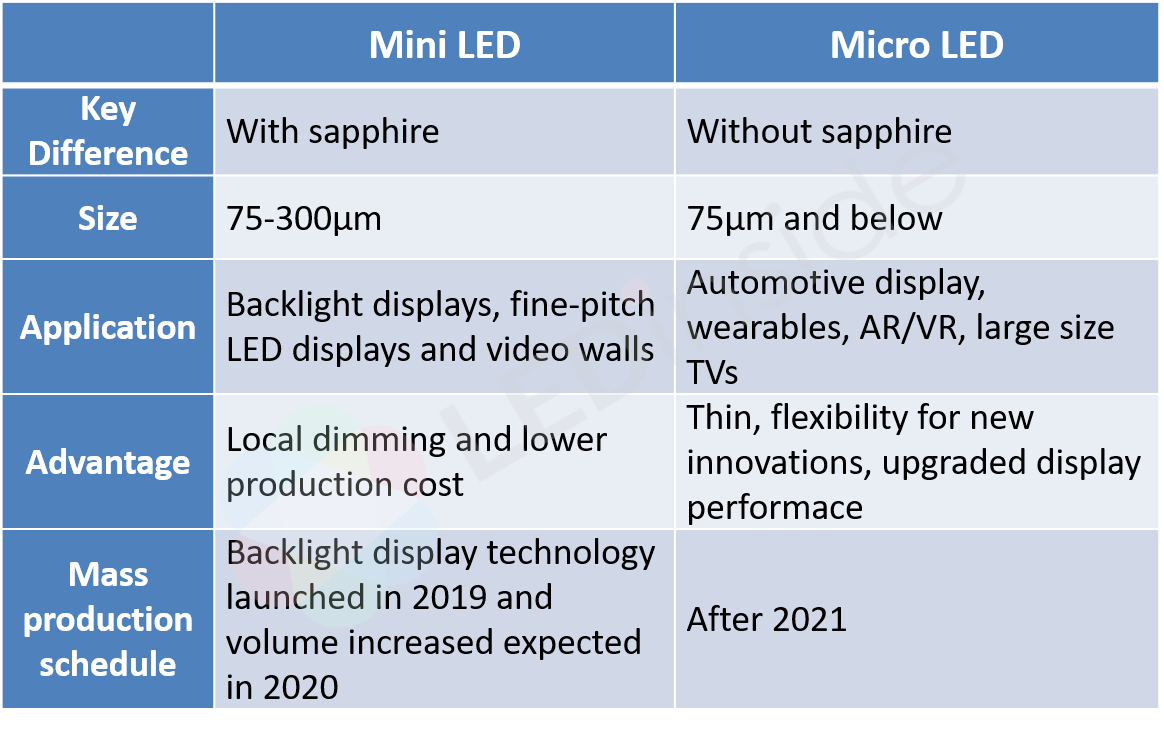
Micro LED display technology, on the other hand, is likely to create innovative applications. Without sapphire substrate, Micro LEDs are lighter, thinner, and could be integrated with different materials. Currently many are working on Micro LED display for AR/VR devices, automotive applications and wearables.
To further materialized the so-called “marvelous” Micro LED displays, at the moment related technology builders set their goal on optimizing manufacture technology and reduce production cost. With even tinier chip size, Micro LEDs require enhanced EQE and semiconductor level equipment to process. Consequently, cooperation between the supply chains is crucial for Micro LED chip manufacture, mass transferring, testing and repairing. Working with semiconductor material and equipment suppliers could be a feasible solution for Micro LED display production as well.
2020 Micro LED Forum will go online and begin broadcasting on July 29 for sharing more Micro LED and Mini LED technology breakthroughs and commercialization progresses. Register now for early bird discount!






 CN
TW
EN
CN
TW
EN








