The efficient conversion of light into electricity plays a crucial role in many technologies, ranging from cameras to solar cells. It also forms an essential step in data communication applications, since it allows for information carried by light to be converted into electrical information that can be processed in electrical circuits. Graphene is an excellent material for ultrafast conversion of light to electrical signals, but so far it was not known how fast graphene responds to ultrashort flashes of light.
 |
|
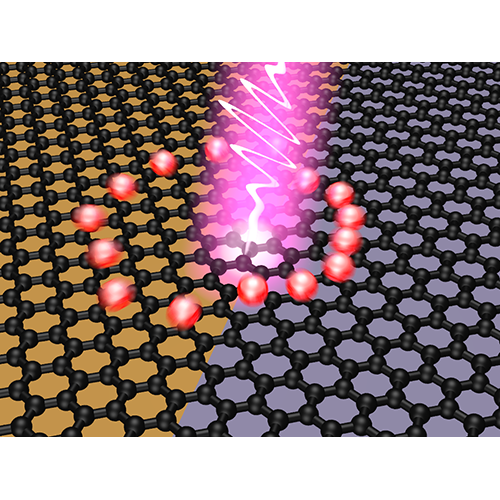
Ultrafast photovoltage creation after light absorption at the interface of two graphene areas with different Fermi energy. (ICFO/LEDinside) |
ICFO researchers Klaas-Jan Tielrooij, Lukasz Piatkowski, Mathieu Massicotte and Achim Woessner, led by ICFO Prof. Frank Koppens and ICREA Prof. at ICFO Niek van Hulst, in collaboration with scientists from the research group led by Pablo Jarillo-Herrero at MIT and the research group led by Jeanie Lau at UC Riverside, have now demonstrated a graphene-based photodetector that converts absorbed light into an electrical voltage at extremely high speeds. The new device is capable of converting light into electricity in less than 50 femtoseconds (a twentieth of a millionth of a millionth of a second). To demonstrate this, researchers used a combination of ultrafast pulse-shaped laser excitation and highly sensitive electrical readout. The study, entitled “Generation of photovoltage in graphene on a femtosecond timescale through efficient carrier heating”, has recently been published in Nature Nanotechnology.
The ultrafast creation of a photovoltage in graphene is possible due to the extremely fast and efficient interaction between all conduction band carriers in graphene. This interaction leads to a rapid creation of an electron distribution with an elevated electron temperature. Thus, the energy absorbed from light is efficiently and rapidly converted into electron heat. Next, the electron heat is converted into a voltage at the interface of two graphene regions with different doping. This photo-thermoelectric effect turns out to occur almost instantaneously, thus enabling the ultrafast conversion of absorbed light into electrical signals.
The results obtained from the findings of this work, which has been partially funded by the EC Graphene Flagship, open a new pathway towards ultra-fast optoelectronic conversion.
This work was funded by the E.C. under Graphene Flagship, as well as an NWO Rubicon fellowship, an ICFO-Cofund fellowship, The Fundacio Cellex Barcelona, the ERC and the MIT MISTI-Spain program.





 CN
TW
EN
CN
TW
EN






